-
33/1, EAST PATEL NAGAR,
NEW DELHI - 110008 -
-
Mon - Sat : 10.00am to 02.00pm
05.00pm to 08.00pm
Dentures
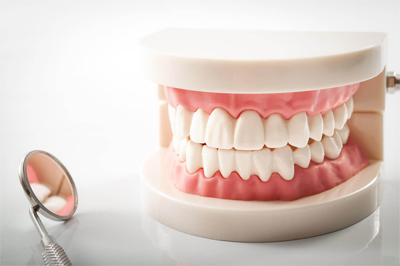 Dentures that replace some but not all of the teeth are known as partial dentures. They attach to the teeth that are still present and also cover and rest on the gums and bone where the teeth are missing. Dental implants can also be used to restore and stabilize partial dentures as well.
Dentures that replace some but not all of the teeth are known as partial dentures. They attach to the teeth that are still present and also cover and rest on the gums and bone where the teeth are missing. Dental implants can also be used to restore and stabilize partial dentures as well.
FAQ's
What types of dentures are there?
Dentures may replace all or only some of the teeth. The dentures that replace all the teeth are known as complete dentures and they rest on the gums that cover the jawbones. The stability and retention of these dentures can be improved by attaching them to dental implants. Dentures that replace some but not all of the teeth are known as partial dentures. They attach to the teeth that are still present and also cover and rest on the gums and bone where the teeth are missing. Dental implants can also be used to restore and stabilize partial dentures as well.
What are permanent dentures?
The term "permanent dentures" is deceptive and misleading. As we know, most things in life are not permanent, teeth and dentures alike. "permanent dentures" are retained by screws or dental cement onto dental implants and cannot be removed by a patient; they can only be removed by your prosthodontist. Eventually even these "permanent dentures" may wear or break or become stained and discolored and will require replacement. Typically, soreness should be resolved within two weeks; if it persists, likely something in the denture needs to be adjusted. You should see your dentist as soon as possible.
How long do dentures last?
Over a period of time, your denture will need to be relined, remade, or rebased due to normal wear. Rebasing means making a new base while keeping the existing denture teeth. Also, as you age, your mouth naturally changes. These changes cause your dentures to loosen, making chewing difficult and irritating your gums. At a minimum, you should see your dentist annually for a check up.
